Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle that makes it more difficult for the heart to deliver blood to the body. This can lead to heart failure.
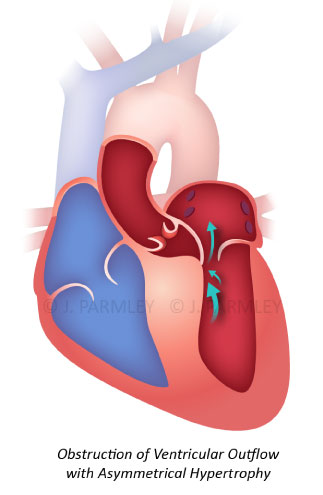
Dilated cardiomyopathy can effect one or all four chambers of the heart (left and right ventricles and atria.) As the heart muscle stretches, or dilates, it becomes less effective at pumping blood. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is characterized by the abnormal thickening of the heart muscle, that’s limited to the left ventricle. The thickened muscle makes it harder for the heart to pump blood.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is characterized by the abnormal thickening of the heart muscle, that’s limited to the left ventricle. The thickened muscle makes it harder for the heart to pump blood.

Stress-induced cardiomyopathy is also known as Takotsubo cardiomyopathy since the shape of the left ventricle and the preserved function of the base resembles an octopus pot, or takotsubo. This type of cardiomyopathy is common with postmenopausal women with a history of recent emotional or physical trauma and the cardiac dysfunction is usually temporary with an excellent long-term prognosis.
